
Both the negative and the positive charges cancel out each other, resulting in a neutral amino acid that behaves as a zwitterion. Thus, at the physiological pH, the carboxylic group of amino acids is ‘deprotonated’ and carries a negative charge, while the amino group is ‘protonated’ and carries a positive charge. At the physiological pH of the human body, the carboxylic group of amino acids easily donates its proton that is immediately accepted by its amino group. As mentioned earlier, all amino acids carry a weak acidic group and a weak basic group. The term zwitterion is used for a molecule that carries both the positive and negative charges and thus, is electrically neutral. The D-amino acids are only found in the bacterial cell wall and some other proteins. The L-amino acids are most common in nature. In the D- form, the amino group is present on the right side while in the L-form, the amino group is present on the left side. Both these isomers are the mirror images of each other and are called stereoisomers or enantiomers. The alpha carbon of all the amino acids is attached to four different groups or atoms and is called a “chiral carbon”, except the alpha carbon of Glycine (it has hydrogen atom as the side chain).ĭue to this chiral behavior of carbon atom, all the amino acids except Glycine can have two isomers, a D-isomer and an L-isomer. The isomers have the same molecular formula but differ in the structural arrangement of their atoms. The term isomerism means the existence of a molecule in more than one form. In this section, we will only discuss some important properties associated with all the amino acids regardless of their side chain (-R). The properties of amino acids are highly dependent on side chain (-R) and are highly variable.

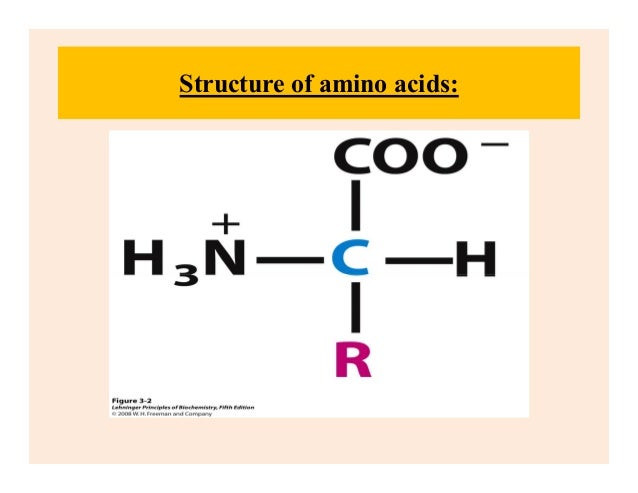
All the twenty amino acids differ from one another in the structure of the side chain (-R). This side chain (-R) may be as simple as a hydrogen atom or it may contain complex functional groups or other atoms. They mainly differ based on the side chain (-R). The first four components are similar in all amino acids. This carbon atom is known as the alpha carbon of amino acids. In the case of amino acids, both the functional groups, the hydrogen atom and the side chain (-R) are all attached to the same carbon atom. Usually, the term alpha is used for the carbon atom to which the main functional group is attached. It is also present in all the amino acids. It is simply a hydrogen atom that is attached to the alpha carbon or central carbon of amino acids. All amino acids carry only one amino group except the basic amino acids that have two amino groups in their structure. It accepts the hydrogen atom donated by the carboxylic group at the physiological pH and thus implies the basic properties to the amino acids. This is the basic functional group present in all amino acids. All amino acids have one carboxylic group in their structure except the acidic amino acids that carry two carboxylic groups. The carboxylic group donates a hydrogen at the normal pH of the body and implies the acidic properties to the amino acids. This is the acidic functional group present in all amino acids. Let us have a little knowledge about these components of amino acids. According to this formula, each amino acid consists of Read more about the structure and properties of 20 amino acids StructureĪll amino acids follow a general structure known as a general formula of amino acids. In this section of notes, we will have a detailed discussion on these 20 amino acids, their structure, properties, classification, chemical bonds, and much more. However, only 20 amino acids are found in the proteins of our body. Out of these amino acids, only 25 are the components of proteins. All these amino acids are required for protein synthesis in the body, which in turn perform all the functions.Īround 170 amino acids are found to be present in the living cells and tissues. Some of the amino acids can be produced by the human body, while others are required to be taken from external sources in the form of diet. They join together to form polymers known as proteins. Which bond is present between amino acids to form proteins?Īmino acids are the organic molecules that act as building blocks of proteins.What is the difference between essential and non-essential amino acids?.How many amino acids are present in the human body?.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
